- 单人版爬虫:一个 Goroutine 运行整个爬虫项目
- 并发版爬虫:多个 Goroutine 在一台机器上实现爬虫项目
- 分布式爬虫:多个 Goroutine 在多台机器上实现爬虫项目
一、爬虫整体算法
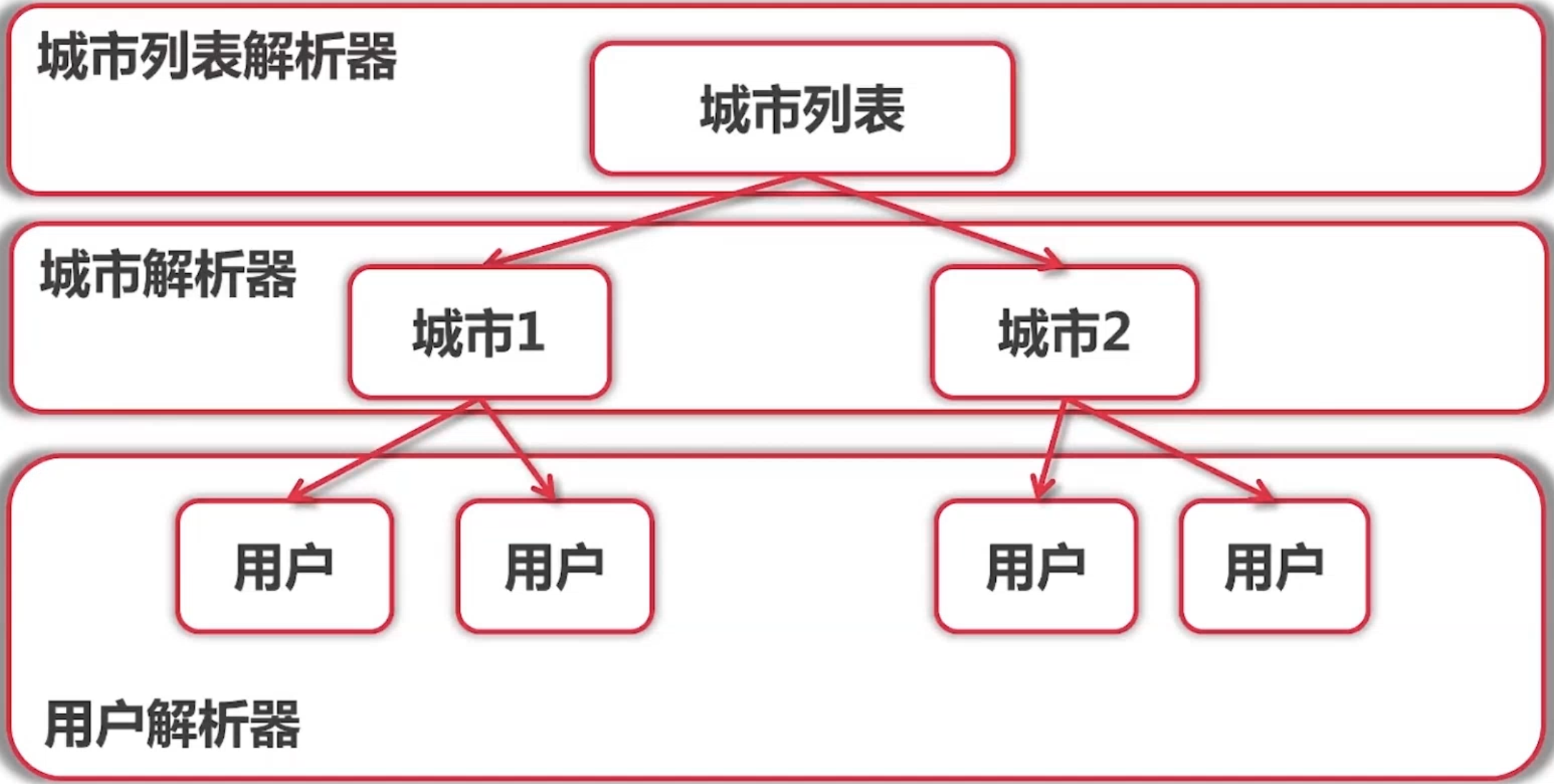
该爬虫项目爬取的是珍爱网的数据,总体算法如下
- 首先根据城市列表 Url 爬取城市列表,爬取出来的内容通过城市列表解析器解析出来每一个城市的 Url
- 然后根据每一个城市的 Url 爬取该城市的用户信息列表,通过城市解析器将用户信息列表中的用户 Url 解析出来
- 最后根据每一个用户的 Url 爬取该用户的详细信息,并进行解析
三种 Url 示例:
- 城市列表 Url:http://www.zhenai.com/zhenghun
- 城市 Url:http://www.zhenai.com/zhenghun/aba
- 用户 Url:http://album.zhenai.com/u/1902329077
二、单任务版爬虫架构
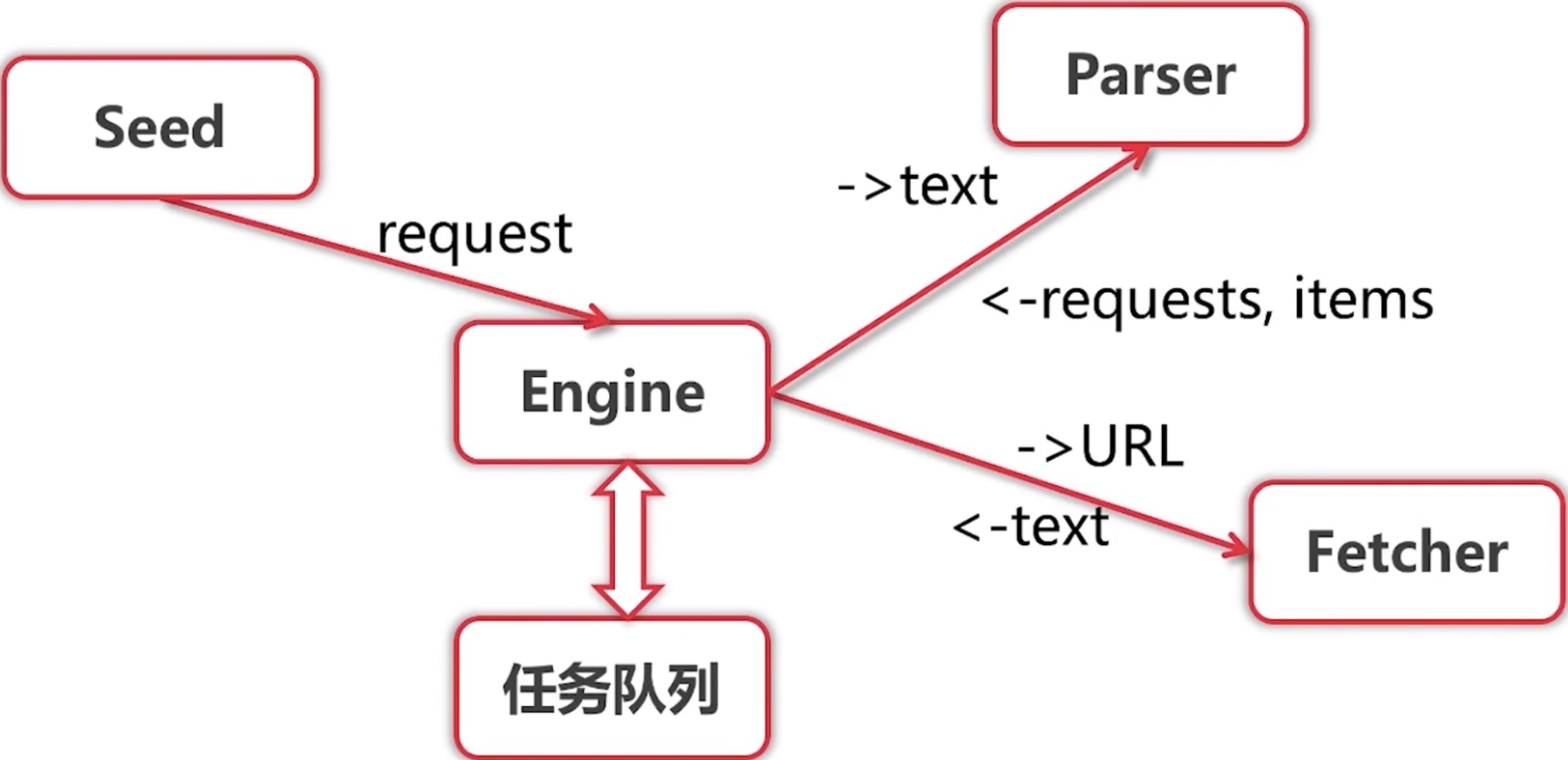
- 1.会将种子 Url Seed 连同其解析器 Parser 封装为一个 Request,放入 Engine 引擎中的任务队列(其实就是 []Request 切片)中,启动爬取任务(这里的 Seed 就是城市列表 Url)
- 2. Engine 使用 Fetcher 爬取该 Url 的内容 text,然后使用对应 Url 的Parser 解析该 text,将解析出来的 Url(例如,城市 Url)和其 Parser 封装为 Request 加入 Engine 任务队列,将解析出来的 items(例如,城市名)打印出来
- 3. Engine 不断的从其任务队列中获取任务 Request 一个个进行串行执行(使用 Fetcher 对 Request.Url 进行爬取,使用 Request.Parser 对爬取出来的 text 进行解析,将解析出来的内容部分进行封装为Request,进行后续循环,部分进行打印)
三、代码实现
3.1 请求与解析结果类型结构 type.go
package engine
// 请求任务封装体
type Request struct {
// 需爬取的 Url
Url string
// Url 对应的解析函数
ParserFunc func([]byte) ParseResult
}
// 解析结果
type ParseResult struct {
// 解析出来的多个 Request 任务
Requests []Request
// 解析出来的实体(例如,城市名),是任意类别(interface{},类比 java Object)
Items []interface{}
}
3.2 执行引擎 engine.go
package engine
import (
"fetcher"
"log"
)
func Run(seeds ...Request) {
// Request 任务队列
var requests []Request
// 将 seeds Request 放入 []requests,即初始化 []requests
for _, r := range seeds {
requests = append(requests, r)
}
// 执行任务
for len(requests) > 0 {
// 1. 获取第一个 Request,并从 []requests 移除,实现了一个队列功能
r := requests[0]
requests = requests[1:]
// 2. 使用爬取器进行对 Request.Url 进行爬取
body, err := fetcher.Fetch(r.Url)
// 如果爬取出错,记录日志
if err != nil {
log.Printf("fetch error, url: %s, err: %v", r.Url, err)
continue
}
// 3. 使用 Request 的解析函数对怕渠道的内容进行解析
parseResult := r.ParserFunc(body)
// 4. 将解析体中的 []Requests 加到请求任务队列 requests 的尾部
requests = append(requests, parseResult.Requests...)
// 5. 遍历解析出来的实体,直接打印
for _, item := range parseResult.Items {
log.Printf("getItems, url: %s, items: %v", r.Url, item)
}
}
}
3.3 爬取器 fetcher.go
package fetcher
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
)
func Fetch(url string) ([]byte, error) {
// 1. 爬取 url
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
if resp.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("wrong statusCode, %d", resp.StatusCode)
}
// 2. 读取响应体并返回
return ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
}
3.4 三种解析器
- 城市列表解析器 citylist.go
package parser
import (
"engine"
"regexp"
)
const cityListRe = `<a href="(http://www.zhenai.com/zhenghun/[0-9a-z]+)"[^>]*>([^<]*)</a>`
// cityList 的 ParserFunc func([]byte) ParseResult
// 解析种子页面 - 获取城市列表
func ParseCityList(contents []byte) engine.ParseResult {
result := engine.ParseResult{}
// 正则表达式:()用于提取
rg := regexp.MustCompile(cityListRe)
allSubmatch := rg.FindAllSubmatch(contents, -1)
// 遍历每一个城市的匹配字段(城市 Url 和城市名),并且将 Url 和城市解析器封装为一个 Request
// 最后将该 Request 添加到 ParseResult 中
for _, m := range allSubmatch {
result.Items = append(result.Items, "city "+string(m[2]))
result.Requests = append(result.Requests, engine.Request{
Url: string(m[1]),
ParserFunc: ParseCity,
})
}
// 返回 ParseResult
return result
}
学习 Go 正则表达式的使用
- 城市解析器 city.go
package parser
import (
"engine"
"regexp"
)
// match[1]=url match[2]=name
const cityRe = `<a href="(http://album.zhenai.com/u/[0-9]+)"[^>]*>([^<]+)</a>`
// 解析单个城市 - 获取单个城市的用户列表
func ParseCity(contents []byte) engine.ParseResult {
result := engine.ParseResult{}
rg := regexp.MustCompile(cityRe)
allSubmatch := rg.FindAllSubmatch(contents, -1)
for _, m := range allSubmatch {
name := string(m[2])
result.Items = append(result.Items, "user "+name)
result.Requests = append(result.Requests, engine.Request{
Url: string(m[1]),
ParserFunc: func(c []byte) engine.ParseResult {
return ParseProfile(c, name) // 函数式编程,使用函数包裹函数
},
})
}
return result
}
学习函数式编程:使用函数包裹函数,即函数的返回值和入参都可以是函数。
- 用户解析器 profile.go
package parser
import (
"github.com/zhaojigang/crawler/engine"
"github.com/zhaojigang/crawler/model"
"regexp"
"strconv"
)
var ageRe = regexp.MustCompile(`<td><span class=""label">年龄:</span>([\d])+岁</td>`)
var incomeRe = regexp.MustCompile(`<td><span class=""label">月收入:</span>([^<]+)</td>`)
// 解析单个人的主页
func ParseProfile(contents []byte, name string) engine.ParseResult {
profile := model.Profile{}
// 1. 年龄
age, err := strconv.Atoi(extractString(contents, ageRe))
if err == nil {
profile.Age = age
}
// 2. 月收入
profile.Income = extractString(contents, incomeRe)
// 3. 姓名
profile.Name = name
result := engine.ParseResult{
Items: []interface{}{profile},
}
return result
}
func extractString(body []byte, re *regexp.Regexp) string {
match := re.FindSubmatch(body) // 只找到第一个match的
if len(match) >= 2 {
return string(match[1])
}
return ""
}
profile 实体类
package model
type Profile struct {
// 姓名
Name string
// 年龄
Age int
// 收入
Income string
}
3.5 启动器 main.go
package main
import (
"github.com/zhaojigang/crawler/engine"
"github.com/zhaojigang/crawler/zhenai/parser"
)
func main() {
engine.Run(engine.Request{
// 种子 Url
Url: "http://www.zhenai.com/zhenghun",
ParserFunc: parser.ParseCityList,
})
}
解析器测试类
package parser
import (
"io/ioutil"
"testing"
)
func TestParseCityList(t *testing.T) {
expectRequestsLen := 470
expectCitiesLen := 470
// 表格驱动测试
expectRequestUrls := []string{
"http://www.zhenai.com/zhenghun/aba",
"http://www.zhenai.com/zhenghun/akesu",
"http://www.zhenai.com/zhenghun/alashanmeng",
}
expectRequestCities := []string{
"city 阿坝",
"city 阿克苏",
"city 阿拉善盟",
}
body, err := ioutil.ReadFile("citylist_test_data.html")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
result := ParseCityList(body)
if len(result.Requests) != expectRequestsLen {
t.Errorf("expect requestLen %d, but %d", expectRequestsLen, len(result.Requests))
}
if len(result.Items) != expectCitiesLen {
t.Errorf("expect citiesLen %d, but %d", expectCitiesLen, len(result.Items))
}
for i, url := range expectRequestUrls {
if url != result.Requests[i].Url {
t.Errorf("expect url %s, but %s", url, result.Requests[i].Url)
}
}
for i, city := range expectRequestCities {
if city != result.Items[i] {
t.Errorf("expect url %s, but %s", city, result.Items[i])
}
}
}
学习经典的 Go 表格驱动测试。
执行 main 函数发现执行的很慢,因为只有一个 main Go routine 在执行,还有网络 IO,所以比较慢,接下来,将单任务版的改造成多个 Go routine 共同执行的并发版的爬虫。