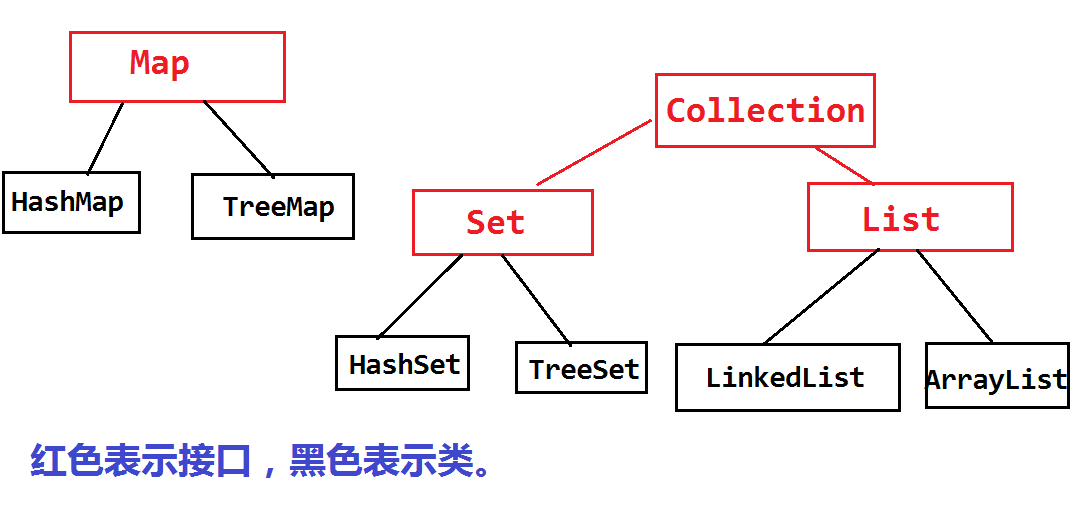
Java集合类如下图:
- set是一个数据集合
- List属于数组列表
- Map也属于一个数据集合
网上找了个图,方便理解。
- List , Set, Map都是接口,前两个继承至Collection接口,Map为独立接口
- Set下有HashSet,LinkedHashSet,TreeSet
- List下有ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList
- Map下有Hashtable,LinkedHashMap,HashMap,TreeMap
- Collection接口下还有个Queue接口,有PriorityQueue类
1.Set对象
Set是最简单的一种集合。集合中的对象不按特定的方式排序,并且没有重复对象。
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
boolean |
add(E e)
Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present (optional operation).
|
boolean |
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this set if they’re not already present (optional operation).
|
void |
clear()
Removes all of the elements from this set (optional operation).
|
boolean |
contains(Object o)
Returns true if this set contains the specified element.
|
boolean |
containsAll(Collection<?> c)
Returns true if this set contains all of the elements of the specified collection.
|
boolean |
equals(Object o)
Compares the specified object with this set for equality.
|
int |
hashCode()
Returns the hash code value for this set.
|
boolean |
isEmpty()
Returns true if this set contains no elements.
|
Iterator<E> |
iterator()
Returns an iterator over the elements in this set.
|
boolean |
remove(Object o)
Removes the specified element from this set if it is present (optional operation).
|
boolean |
removeAll(Collection<?> c)
Removes from this set all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation).
|
boolean |
retainAll(Collection<?> c)
Retains only the elements in this set that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation).
|
int |
size()
Returns the number of elements in this set (its cardinality).
|
default Spliterator<E> |
spliterator()
Creates a
Spliterator over the elements in this set. |
Object[] |
toArray()
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set.
|
<T> T[] |
toArray(T[] a)
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array.
|
HashSet
HashSet底层用的是哈希表,它把对象根据其哈希值存放到对应的区域里。由于这种特性,两个在不同区域的对象会被认为不相同的。
所以如果对象要存放到Hash集合里面,则需要重写对象的hashCode方法,让相等的对象的hashCode的值也相等。
TreeSet
TreeSet采用的数据结构是红黑树,我们可以让它按指定规则对其中的元素进行排序。它又是如何判断两个元素是否相同呢?除了用equals方法检查两个元素是否相同外,还要检查compareTo方法是否返回为0。
所以如果对象要存放到Tree集合里,需要在重写compareTo方法,把相同的对象的比较值定为0,防止相同的元素被重复添加进集合中。
LinkedHashSet
底层数据结构是链表和哈希表。(FIFO插入有序,唯一)
- 由链表保证元素有序
- 由哈希表保证元素唯一
set的测试:
Set<String> data = new TreeSet<>(); data.add("re"); data.add("idn"); data.add("mob"); data.add("ref"); data.add("01"); out(data); Set<Integer> integers = new TreeSet<>(); integers.add(12); integers.add(1); integers.add(15); integers.add(5); integers.add(65); out(integers);
打印结果如下:
[01, idn, mob, re, ref]
[1, 5, 12, 15, 65]
2.List对象
List 接口继承了 Collection 接口以定义一个允许重复项的有序集合。该接口不但能够对列表的一部分进行处理,还添加了面向位置的操作。
有序的 collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
boolean |
add(E e)
Appends the specified element to the end of this list (optional operation).
|
void |
add(int index, E element)
Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list (optional operation).
|
boolean |
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection’s iterator (optional operation).
|
boolean |
addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this list at the specified position (optional operation).
|
void |
clear()
Removes all of the elements from this list (optional operation).
|
boolean |
contains(Object o)
Returns true if this list contains the specified element.
|
boolean |
containsAll(Collection<?> c)
Returns true if this list contains all of the elements of the specified collection.
|
boolean |
equals(Object o)
Compares the specified object with this list for equality.
|
E |
get(int index)
Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
|
int |
hashCode()
Returns the hash code value for this list.
|
int |
indexOf(Object o)
Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
|
boolean |
isEmpty()
Returns true if this list contains no elements.
|
Iterator<E> |
iterator()
Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence.
|
int |
lastIndexOf(Object o)
Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
|
ListIterator<E> |
listIterator()
Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence).
|
ListIterator<E> |
listIterator(int index)
Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence), starting at the specified position in the list.
|
E |
remove(int index)
Removes the element at the specified position in this list (optional operation).
|
boolean |
remove(Object o)
Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, if it is present (optional operation).
|
boolean |
removeAll(Collection<?> c)
Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation).
|
default void |
replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator)
Replaces each element of this list with the result of applying the operator to that element.
|
boolean |
retainAll(Collection<?> c)
Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation).
|
E |
set(int index, E element)
Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element (optional operation).
|
int |
size()
Returns the number of elements in this list.
|
default void |
sort(Comparator<? super E> c)
Sorts this list according to the order induced by the specified
Comparator. |
default Spliterator<E> |
spliterator()
Creates a
Spliterator over the elements in this list. |
List<E> |
subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive.
|
Object[] |
toArray()
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper sequence (from first to last element).
|
<T> T[] |
toArray(T[] a)
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array.
|
ArrayList
- 优点: 底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢。
- 缺点: 线程不安全,效率高
Vector
- 优点: 底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢。
- 缺点: 线程安全,效率低
LinkedList
- 优点: 底层数据结构是链表,查询慢,增删快。
- 缺点: 线程不安全,效率高
PS:ArrayList是实现了基于底层的数据结构,LinkedList基于底层数据结构是链表;对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList觉得优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList遍历全部再确定;对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。
Collection是集合接口
|————Set子接口:无序,不允许重复。
|————List子接口:有序,可以有重复元素。
区别:Collections是集合类
Set和List对比:
- Set:检索元素效率低下,删除和插入效率高,插入和删除不会引起元素位置改变。
- List:和数组类似,List可以动态增长,查找元素效率高,插入删除元素效率低,因为会引起其他元素位置改变。
List的排序示例:
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(12);
list.add(1);
list.add(15);
list.add(5);
list.add(65);
list.sort((a,b)->{
return a-b;
});
out(list);
打印结果:
[1, 5, 12, 15, 65]
如果降序,只需要把a-b改成b-a即可。
3.Map对象
Map 是一种把键对象和值对象映射的集合,它的每一个元素都包含一对键对象和值对象。 Map没有继承于Collection接口 从Map集合中检索元素时,只要给出键对象,就会返回对应的值对象。
map主要的特性:
- key字段不可重复
- key,value 都可以是任何引用类型的数据,包括 null
- Map 取代了古老的 Dictionary 抽象类
因此,每个 key 只能对应一个 value, 多个 key 可以对应一个 value。Map集合维护“键、值对”的关联性,使你可以通过“键”查找“值”。
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
void |
clear()
Removes all of the mappings from this map (optional operation).
|
default V |
compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction)
Attempts to compute a mapping for the specified key and its current mapped value (or
null if there is no current mapping). |
default V |
computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? extends V> mappingFunction)
If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to
null), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping function and enters it into this map unless null. |
default V |
computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction)
If the value for the specified key is present and non-null, attempts to compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value.
|
boolean |
containsKey(Object key)
Returns true if this map contains a mapping for the specified key.
|
boolean |
containsValue(Object value)
Returns true if this map maps one or more keys to the specified value.
|
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> |
entrySet()
Returns a
Set view of the mappings contained in this map. |
boolean |
equals(Object o)
Compares the specified object with this map for equality.
|
default void |
forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action)
Performs the given action for each entry in this map until all entries have been processed or the action throws an exception.
|
V |
get(Object key)
Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or
null if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
default V |
getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue)
Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or
defaultValue if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
int |
hashCode()
Returns the hash code value for this map.
|
boolean |
isEmpty()
Returns true if this map contains no key-value mappings.
|
Set<K> |
keySet()
Returns a
Set view of the keys contained in this map. |
default V |
merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction)
If the specified key is not already associated with a value or is associated with null, associates it with the given non-null value.
|
V |
put(K key, V value)
Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map (optional operation).
|
void |
putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m)
Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map (optional operation).
|
default V |
putIfAbsent(K key, V value)
If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to
null) associates it with the given value and returns null, else returns the current value. |
V |
remove(Object key)
Removes the mapping for a key from this map if it is present (optional operation).
|
default boolean |
remove(Object key, Object value)
Removes the entry for the specified key only if it is currently mapped to the specified value.
|
default V |
replace(K key, V value)
Replaces the entry for the specified key only if it is currently mapped to some value.
|
default boolean |
replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue)
Replaces the entry for the specified key only if currently mapped to the specified value.
|
default void |
replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> function)
Replaces each entry’s value with the result of invoking the given function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the function throws an exception.
|
int |
size()
Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map.
|
Collection<V> |
values()
Returns a
Collection view of the values contained in this map. |
Map的功能方法
- put(Object key, Object value)添加一个“值”(想要得东西)和与“值”相关联的“键”(key)(使用它来查找)。
- get(Object key)返回与给定“键”相关联的“值”。
- containsKey()和containsValue()可以检查Map中是否包含某个“键”或“值”。
标准的Java类库中包含了几种不同的Map:
HashMap, TreeMap, LinkedHashMap, WeakHashMap, IdentityHashMap。
它们都有同样的基本接口Map,但是行为、效率、排序策略、保存对象的生命周期和判定“键”等价的策略等各不相同。
执行效率是Map的一个大问题,看看get方法的代码,就会明白为什么在ArrayList中搜索“键”是相当慢的。而这正是HashMap提高速度的地方。HashMap使用了特殊的值,称为“散列码”(hash code),来取代对键的缓慢搜索。“散列码”是“相对唯一”用以代表对象的int值,它是通过将该对象的某些信息进行转换而生成的。所有Java对象都能产生散列码,因为hashCode()是定义在基类Object中的方法。
HashMap
Map基于散列表的实现,就是使用对象的hashCode()进行快速查询的,插入和查询“键值对”的开销是固定的,此方法能够显着提高性能。
LinkedHashMap
类似于HashMap,但是迭代遍历它时,取得“键值对”的顺序是其插入次序,或者是最近最少使用(LRU算法)的次序;只比HashMap慢一点,而在迭代访问时发而更快,因为它使用链表维护内部次序。
TreeMap
基于红黑树数据结构的实现,查看“键”或“键值对”时,它们会被排序(次序由Comparabel或Comparator决定)。TreeMap的特点在于,你得到的结果是经过排序的。TreeMap是唯一的带有subMap()方法的Map,它可以返回一个子树。
WeakHashMao
弱键(weak key)Map,Map中使用的对象也被允许释放: 这是为解决特殊问题设计的。如果没有map之外的引用指向某个“键”,则此“键”可以被垃圾收集器回收。
IdentifyHashMap
使用==代替equals()对“键”作比较的hash map,专为解决特殊问题而设计。
总结
List,Set,Map将持有对象一律视为Object型别;Collection、List、Set、Map都是接口,不能实例化。继承自它们的 ArrayList, Vector, HashTable, HashMap是具体的对象,可被实例化。vector容器确切知道它所持有的对象隶属什么型别,vector不进行边界检查。
注意:
- 如果涉及到堆栈,队列等操作,应该考虑用List,对于需要快速插入,删除元素,应该使用LinkedList,如果需要快速随机访问元素,应该使用ArrayList。
- 如果程序在单线程环境中,或者访问仅仅在一个线程中进行,考虑非同步的类,其效率较高,如果多个线程可能同时操作一个类,应该使用同步的类。
- 在除需要排序时使用TreeSet、TreeMap外,其他应使用HashSet,HashMap,因为他们的效率更高。
- 要特别注意对哈希表的操作,作为key的对象要正确复写equals和hashCode方法。
- 容器类仅能持有对象引用(指向对象的指针),而不是将对象信息copy一份至数列某位置,一旦将对象置入容器内,便损失了该对象的型别信息。
- 尽量返回接口而非实际的类型,如返回List而非ArrayList,这样如果以后需要将ArrayList换成LinkedList时,客户端代码不用改变。这就是针对抽象编程。
- Collection没有get()方法来取得某个元素。只能通过iterator()遍历元素。
- Set和Collection拥有一模一样的接口。
- List,可以通过get()方法来一次取出一个元素。
- 一般使用ArrayList;用LinkedList构造堆栈stack、队列使用queue。
- Map用 put(k,v) / get(k),还可以使用containsKey()/containsValue()来检查其中是否含有某个key
F{0XCAB)LKNIT0K@G.gif) 、alue。
、alue。 - HashMap会利用对象的hashCode来快速找到key。
- Map中元素,可以将key序列、value序列单独抽取出来。
- 使用keySet()抽取key序列,将map中的所有keys生成一个Set。
- 使用values()抽取value序列,将map中的所有values生成一个Collection。
- 为什么一个生成Set,一个生成Collection呢?因为,key总是独一无二的,value允许重复。


近期评论